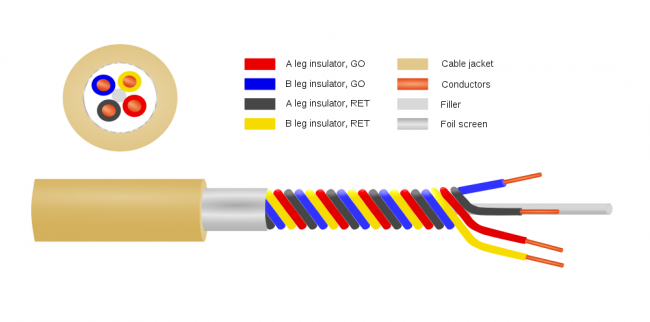
Over the years, I have collected many pinouts for all sorts of interfaces, connectors, jacks, etc. These are all stored on my laptop and on my smartphone. It is easy enough to look these things up online, however, there are occasions when the internet is not available for whatever reason. Thus, this is my collection of pinouts, many of which have been adapted from Wikipedia articles. Many times I put things here for my own use. However, if I have spent ten minutes looking for the USB pin out on my smartphone, someone else has done the same thing. Most of these images have higher resolutions available.
Enjoy!
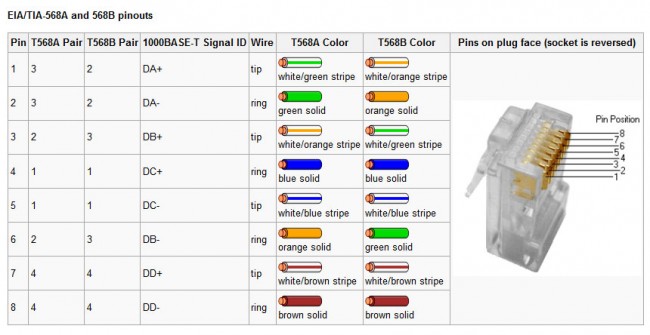
Standard networking connectors for Ethernet connections. Rumor has it that only the “A” standard is accepted for government work and the “B” standard is being depreciated.
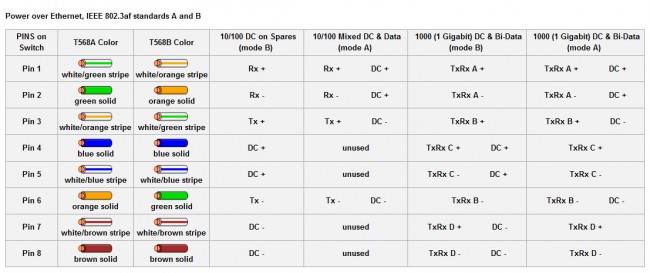
Power over Ethernet pinouts. More and more commonly used in VOIP phone systems, but can also be found in wireless access points and other things of that nature.
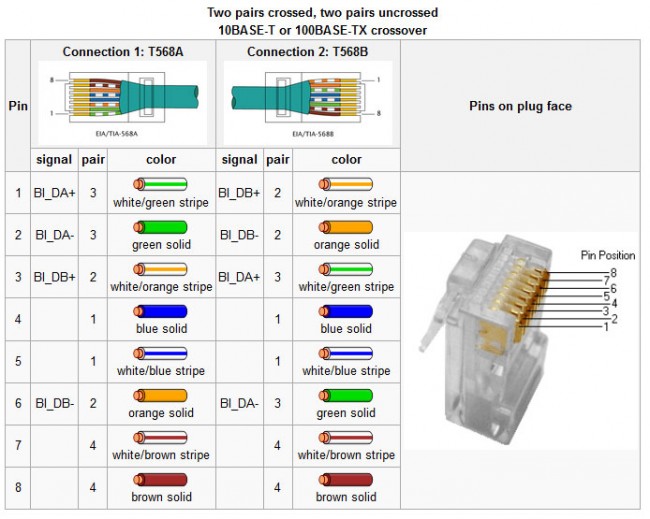
Ethernet crossover cables are useful for connecting to similar pieces of equipment together, e.g. a computer to a computer, or a switch to a switch. Many new switches have port sensing, which will automatically cross the connection if a straight through cable is used. Others have a specific port or a switch for a specific port which will cross over the cable. Gigabit Ethernet uses all four pairs, thus a 1000 base T crossover looks a little bit different.
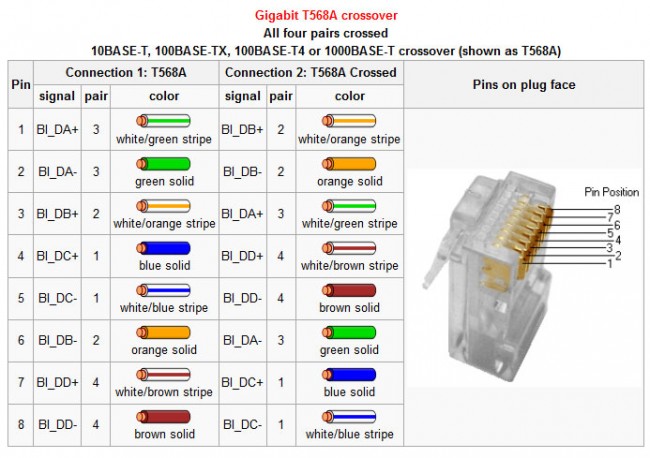
This type cable is backwards compatible with 10/100 base T systems.
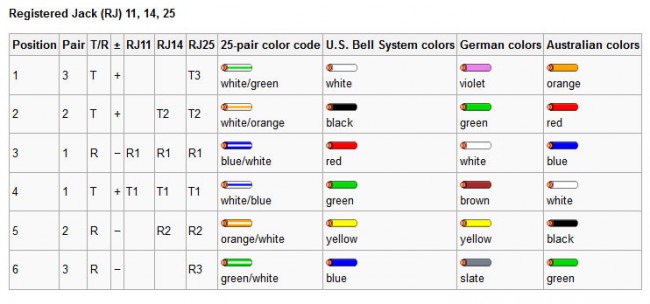
Telephone system equipment jacks.
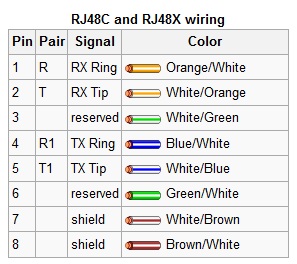
RJ48 and 48X used on T-1 (DS-1) and ISDN connections. Since BRI and PRI ISDN are two wire circuits, the active pins are 4/5, which is the same as an RJ11. I have often used RJ11 jacks for ISDN and found no issues with doing so.
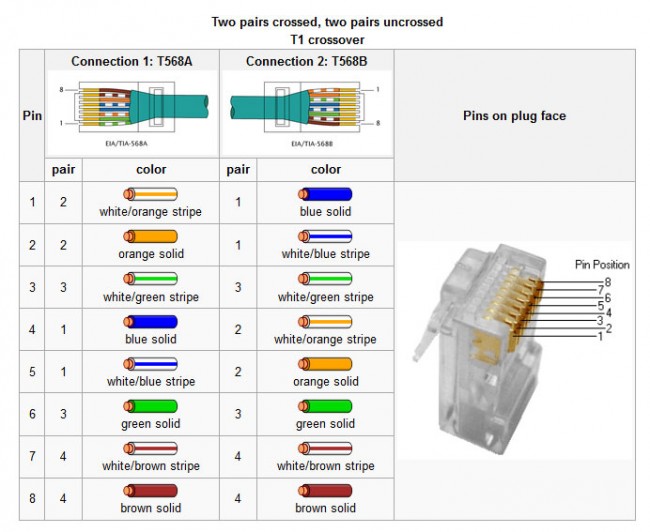
Crossover cable for T-1 (DS-1 or DSX-1 interface). Note, this is different from an Ethernet crossover cable, which will not work for in a DS-1 interface. A T-1 loopback connector goes from pin 1 to pin 4 and pin 2 to pin 5 on a 8P8C connector.
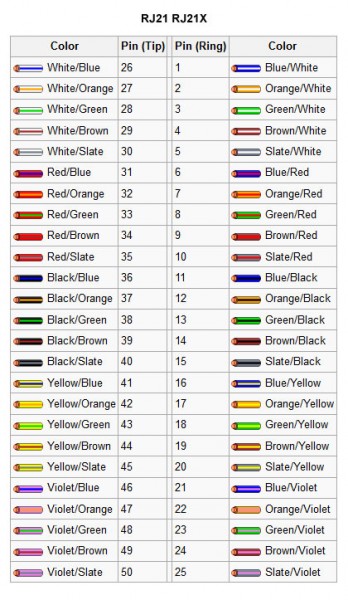
RJ21 and 21X connectors are often found on the side of punch blocks and make for quick connections on cabling trunks.

The generic 25 pair color code, which is always a good thing to have.
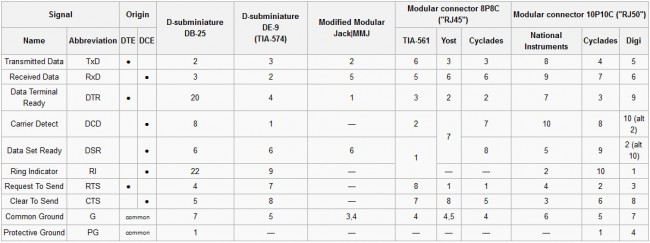
RS-232 is still commonly used for data transfer in broadcast facilities. RS-485 is also used, however, that standard is often used with screw terminals or some other generic connection.
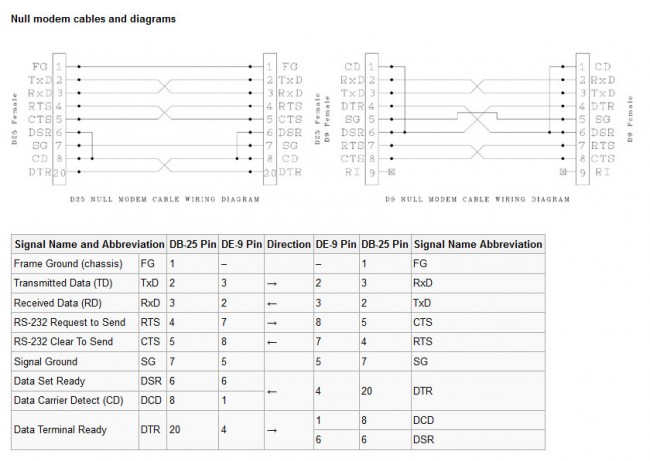
Null modems for connecting equipment together and testing.
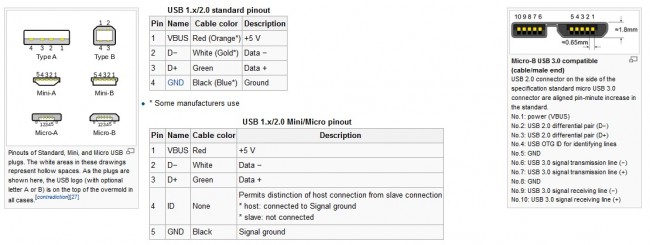
Various USB connectors and pinouts. USB has replaced RS-232 data ports on most newer computers.
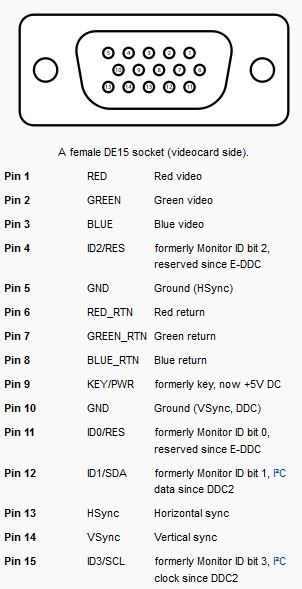
Computer graphics card pinouts.
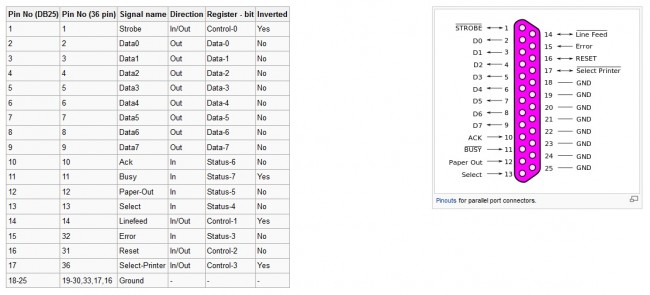
Computer parallel port pinout, not used very much anymore, replace by mostly USB devices. Can also be used as a limited GPI/GPO interface. Some small automation software programs use pins 10,11,12,13 and 15 for closure information and pins 1, 14, 16, and 17 for output switching, machine starts and the like.
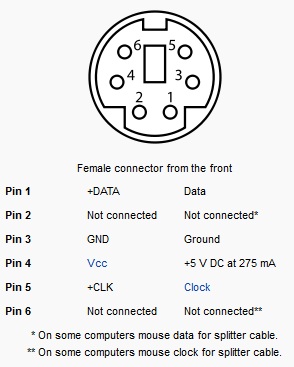
PS2 mouse and keyboard connectors, again, replaced by USB but still found on older motherboards.

RJ-45 to balanced audio. This is a fairly standardized audio application for RJ-45 connectors developed by Radio Systems/Studio Hub. It is also used by Telos/Axia and Wheatstone, although often the +/- 15 VDC power is not included.
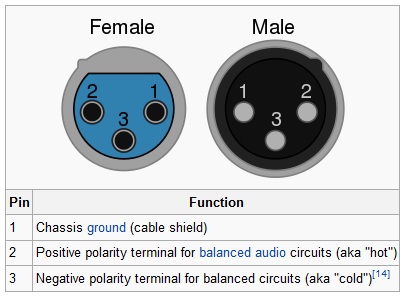
The ubiquitous XLR connector, still used for analog audio and also AES/EBU digital audio.